Did you know that life cycle analysis (LCA) is a global standard? It’s recognized by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO 14040 series)1. This tool helps in research and innovation in environmental science and sustainable technologies1. It also gives insights into product design, manufacturing, and waste management, reducing environmental impact and improving efficiency1.
As businesses face today’s market challenges, understanding industry life cycle analysis is key. It helps in making strategic decisions and staying competitive.
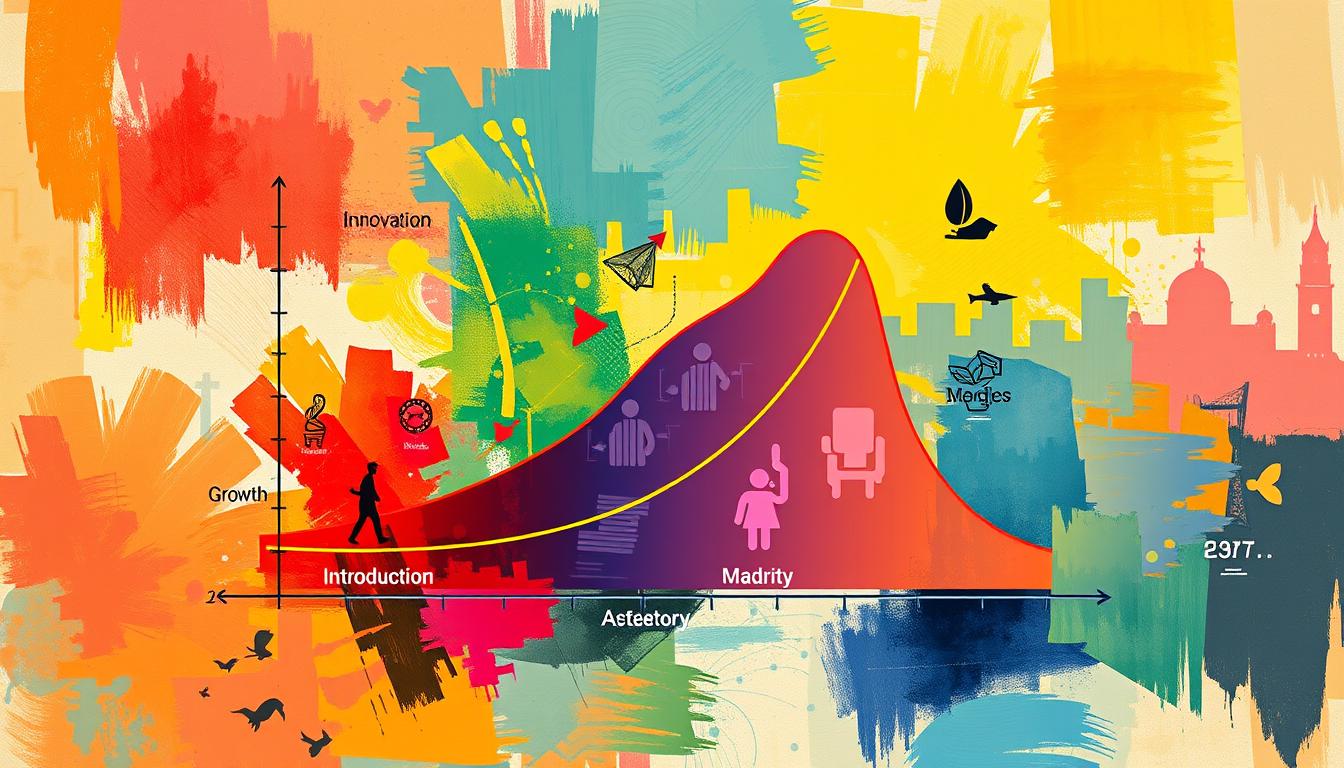
Industry life cycle analysis breaks down into four stages: introduction, growth, maturity, and decline2. This framework helps companies see challenges and opportunities ahead. By using industry life cycle analysis, businesses can make smart choices, understand the competition, and adjust to new trends.
Key Takeaways
- Industry life cycle analysis provides a structured framework for understanding the evolution of industries and their associated market dynamics.
- Analyzing the life cycle stages of an industry enables businesses to anticipate challenges, capitalize on opportunities, and maintain a competitive edge.
- Monitoring key financial metrics, such as sales, profits, and cash flows, is important in each phase of the industry life cycle.
- Adopting an industry life cycle perspective helps companies make strategic decisions based on changing market conditions and trends.
- Using life cycle analysis in business strategy can lead to better product design, manufacturing, and waste management. This improves efficiency and sustainability.
Understanding Industry Life Cycle Fundamentals
The industry life cycle is key for businesses to grasp. It helps them navigate their markets. It has four stages: introduction, growth, maturity, and decline. Each stage has its own market dynamics, competitive pressures, and strategies3.
Defining Industry Life Cycle Stages
In the introduction stage, sales grow slowly and costs are high. As the industry grows, sales and profits increase, but competition gets fiercer. In the maturity stage, the market is saturated, leading to consolidation and focus on efficiency. The decline phase sees sales drop, profit margins shrink, and companies may leave the market3.
Key Components of Life Cycle Analysis
Life cycle analysis looks at sales growth, profit margins, market saturation, and innovation4. These factors help businesses understand their industry’s growth. This knowledge guides decisions on market entry, investment, and long-term planning3.
Impact on Business Strategy
Knowing the industry life cycle is vital for business strategies. Companies must adjust their plans based on the industry stage. This includes product development, marketing, resource use, and expansion plans4. Understanding the industry’s growth helps businesses predict market trends, find opportunities, and stay competitive3.
“The industry life cycle is a powerful tool for businesses to understand the evolution of their market and align their strategies. By recognizing the unique characteristics of each stage, companies can make informed decisions that drive growth, maintain competitiveness, and ensure long-term sustainability.”
The Four Phases of Industry Evolution
The industry life cycle has four main stages: introduction, growth, maturity, and decline5. Knowing these stages helps businesses prepare for market changes and succeed.
The introduction phase is all about product development and uncertainty5. As it grows, demand rises, markets expand, and leaders emerge5.
In the maturity phase, growth slows down, and focus shifts to being efficient5. When the industry declines, demand falls, margins shrink, and exit becomes a thought5.
Each stage brings its own challenges and chances for growth5. By understanding these patterns, companies can handle industry growth, market maturity, business decline, and economic cycles better5.

“The innovator has the most to lose as many new products fail at the introductory stage of the product life cycle after investments have been made in research, development, and production.” – Harvard Business Review, 19656
Successful businesses adapt to the industry life cycle by predicting market changes and seizing growth chances5. By grasping the details of each phase, companies can make smart choices and lead the way5.
| Industry Life Cycle Stage | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Introduction | Product development, market uncertainty, high fragmentation |
| Growth | Rapid demand increase, market expansion, emerging key players |
| Maturity | Slowing growth, consolidation, focus on efficiency |
| Decline | Decreasing demand, margin pressure, possible market exit |
By grasping and predicting the four stages of industry evolution, businesses can better navigate industry growth, market maturity, business decline, and economic cycles for success576.
Strategic Implementation During Introduction Phase
The introduction phase of the industry life cycle is all about market entry, product innovation, and initial market positioning. Companies need to develop and improve their offerings. They also have to teach consumers about their value. Miloriano’s case studies show how startups use these strategies to enter new markets.
Market Entry Tactics
Getting into the market during the introduction phase requires smart marketing, partnerships, and rewards for early users8. Companies must make their brand known and show the special benefits of their products. Partnerships can open up new channels and customers.
Innovation and Product Development
Innovation is key in the introduction phase, with a focus on R&D and quick product updates8. Companies need to keep improving their products to meet changing customer needs and stay competitive9. This phase is all about constant innovation and flexible production.
Initial Market Positioning
Setting the right market position is vital for standing out and showing value8. Marketing strategies focus on building the brand and teaching consumers about the product’s benefits9. Being the first to market can give companies an edge.
The introduction phase is often full of competition and low profits. Companies spend a lot on development and marketing, but earnings are small8. But, those who do well in this phase can set themselves up for future success and leadership.
| Key Strategies | Outcomes |
|---|---|
| Market Entry Tactics | Increased brand recognition, access to new distribution channels, and incentives for early adopters |
| Innovation and Product Development | Continuous product refinement, addressing evolving customer needs, and staying ahead of the competition |
| Initial Market Positioning | Differentiated offer, unique value proposition, and first-mover advantages |
“The introduction phase is a critical period for startups and new products, requiring a strategic and innovative approach to succeed in the long run.”
Growth Phase Opportunities and Challenges
As businesses grow, they face many chances and hurdles. The industry life cycle has four stages: introduction, growth, maturity, and decline3. This growth stage is filled with fast-growing demand, fierce competition, and the need to grow efficiently3. Companies must focus on market expansion, competitive advantage, and scaling operations to use disruptive innovation chances well.
One big chance in the growth phase is to quickly grow market share and reach more places. Harvard professor Michael Porter says 19% of a company’s profit comes from its industry10. Big competitors often join in by buying or creating new companies, making it key for businesses to stand out and build a strong brand3. To succeed, companies focus on strong customer ties, better supply chains, and constant innovation.
But, the growth phase also has big challenges. Fast growth can use up resources, mess with operations, and test how flexible a company is. Managing people, improving productivity, and keeping quality high are key as a business grows. In the maturity phase, prices matter more because products are less different, and cutting costs and focusing on profit is key3. Companies must deal with these issues while also finding new products, services, and markets to stay ahead and keep growing.
The growth phase is a time of big change that needs quick thinking, top-notch operations, and never-ending innovation. By using the chances and tackling the challenges, businesses can strengthen their place in the market and keep growing.

“In advanced economies, most industries have a life cycle length of 35-40 years, with some below 35 years and others over 70 years.”10
Industry Life Cycle Analysis: Adapting to Business Trends
Understanding the business world’s changes is key. Industry life cycle analysis helps companies see market trends, the competition, and new tech. This way, they can grow and stay ahead1.
Market Dynamic Assessment
Adapting starts with knowing the market. Companies need to watch what customers want, new tech, and rules. These things can change the game2.
By keeping an eye on these trends, companies can spot new chances and challenges. This helps them stay on top of the market.
Competitive Landscape Analysis
Knowing who you’re up against is vital. Looking at what rivals do and how they stand helps companies find their own strengths and weaknesses11. This knowledge lets them make plans that play to their strengths and stand out.
Technology Integration Strategies
Using new tech is a big part of adapting. It makes things run smoother, products better, and offers more value to customers1. Being quick to adopt new tech keeps companies ahead of the game.
To really adapt, companies need to understand the market, their rivals, and new tech. By always looking at these areas, they can succeed in a changing world2.
“Adapting to industry life cycle changes is not just a one-time event, but a continuous process of anticipation, evaluation, and strategic pivoting. The companies that thrive are those that can efficiently navigate the ebb and flow of industry dynamics.”
Navigating the Maturity Phase
When an industry reaches the maturity phase, companies need to focus on being more efficient and cutting costs12. This stage is marked by slower growth, more competition, and a full market. It demands a smart plan to stay ahead.
Product differentiation is a key strategy in this phase. Companies must make their products stand out. This helps them keep their brand strong and offer unique value to customers13. Building strong brands and keeping customers loyal is vital to stay competitive.
Market consolidation is common in the maturity phase. This means more mergers and acquisitions as companies try to grow and become more efficient12. They might also expand globally or enter new markets to use their strengths.
Keeping profits high is a big goal in the maturity phase. Companies focus on making their operations smoother and their supply chains better12. They look for small improvements and ways to make things cheaper, aiming to stay competitive.
“Navigating the maturity phase requires a delicate balance of operational efficiency, brand differentiation, and strategic diversification to sustain long-term growth and profitability.”
Understanding the maturity phase’s challenges and chances helps companies stay on top. They can improve their operations, stand out with their brand, and plan for future success13.
Managing Business During Industry Decline
When industries decline, companies face big challenges. They need to be quick to business restructuring, market exit planning, and industry reinvention. This is key to staying alive and growing14.
Restructuring Strategies
During decline, demand drops and technology becomes outdated. Businesses must make hard choices14. They might downsize, sell off parts of the business, or strategic pivoting to new markets. This helps cut costs and stay competitive14.
Market Exit Planning
For some, it’s time to leave the market. Good market exit planning aims to get the most value and lose the least. This could mean selling assets, clearing inventory, or getting good deals with suppliers and customers14.
Innovation for Survival
Innovation is key to surviving decline. Companies need to try new things, like new tech or business models. By strategic pivoting, they can create new products or serve new markets. Businesses that succeed focus on great service, unique products, or big changes14.
Dealing with decline needs careful cost management, smart moves, and new ideas. By tackling these challenges, companies can not only survive but thrive in the long run14.
“Companies facing industry decline must be proactive in business restructuring, market exit planning, and industry reinvention to ensure survival and growth.”
Industry Life Cycle Performance Metrics
Understanding a business’s performance at each stage of its life cycle is key for making smart decisions. As companies move from start to decline, they watch different metrics. These metrics change to meet the challenges and chances of each stage3.
In the early stages, focus is on getting into the market, how much it costs to get customers, and how fast sales grow15. This helps new businesses see if they’re getting more customers and growing. When industries grow older, the focus turns to market share, profit margins, and how well things run3.
In decline, companies look at keeping cash flow good, cutting costs, and using assets well. At all times, they watch sales, profits, return on investment, and how they stack up against rivals15.
These metrics are important for checking how well a company is doing against others. By matching their metrics to the life cycle stage, companies can aim for lasting success3.
“Understanding and adapting to the evolving performance metrics throughout the industry life cycle is essential for businesses to thrive in a dynamic market environment.” – Industry Analyst, XYZ Consulting
For any company, no matter the stage, looking at its life cycle metrics is very helpful. It gives insights for making better decisions and growing in the long run15.
Future-Proofing Your Business Strategy
In today’s fast-changing business world, it’s key to future-proof your strategy. This means being agile and forward-thinking. By doing so, you can handle future challenges and grab new chances.
Emerging Technology Adoption
Using new tech like AI, blockchain, and IoT can boost your business. BCG says adaptable companies are 75% more profitable.16 By leading in tech, you can innovate, work better, and please your customers more.
Market Trend Analysis
Keeping an eye on market trends is vital. Forbes says agile firms get to market 60% faster.16 With data, you can make smart choices, spot new chances, and keep up with trends.
Strategic Pivoting Methods
Being able to change your business plan is essential. This means being agile and open to new ideas. By being adaptable, you can move with industry changes and find new growth paths.
Good future-proofing mixes today’s needs with tomorrow’s chances. By using technological disruption, market forecasting, business agility, and strategic foresight, your business can grow strong and flexible.
“The best way to predict the future is to create it.” – Peter Drucker
Conclusion
Industry life cycle analysis is a key tool for businesses to keep up with changes. It helps companies understand each stage and plan for growth17. By adapting their strategies, businesses can stay ahead and grow17.
Knowing how to react to changes is vital for success in today’s fast-paced world17. Strategic planning and understanding market changes are essential17. This way, companies can lead in their markets.
Adaptability, innovation, and a proactive approach are critical1718. Businesses that adopt these strategies will do well in the changing business world. They will be ready to seize new chances as they come.
FAQ
What is industry life cycle analysis and why is it important?
What are the four primary stages of the industry life cycle?
How does the industry life cycle impact business strategy?
What are the key characteristics and strategic focus areas of the introduction phase?
What are the opportunities and challenges in the growth phase?
How can companies adapt to evolving business trends?
What are the key characteristics and strategic focus areas of the maturity phase?
How can companies manage their business during industry decline?
What are the key performance metrics across the industry life cycle stages?
How can companies future-proof their business strategies?
Source Links
- Everything you need to know about LCA (Life Cycle Analysis) – https://greenly.earth/en-us/blog/company-guide/everything-you-need-to-know-about-lca-life-cycle-analysis-in-2022
- What is a Product Life Cycle Analysis and Management – AI Digital Marketing Agency – https://matrixmarketinggroup.com/product-life-cycle-analysis/
- Understanding the Industry Life Cycle: Phases and Examples – https://www.investopedia.com/terms/i/industrylifecycle.asp
- How to Conduct an Industry Analysis? Template, Examples | Appinio Blog – https://www.appinio.com/en/blog/market-research/industry-analysis
- Industry Life Cycle – https://corporatefinanceinstitute.com/resources/management/industry-life-cycle/
- What is a Product Life Cycle? (Definition, Stages and Examples) – https://www.twi-global.com/technical-knowledge/faqs/what-is-a-product-life-cycle
- What Are the Four Stages of Business Growth? – https://www.jec-llc.com/blog/stages-of-business-growth
- The Ultimate Guide to Understanding Product Life Cycles – https://www.launchnotes.com/blog/the-ultimate-guide-to-understanding-product-life-cycles
- Microsoft Word – ML13-300.doc – https://toknowpress.net/ISBN/978-961-6914-02-4/papers/ML13-300.pdf
- Understanding Industry Life Cycles – https://www.ibisworld.com/blog/understanding-industry-life-cycles/99/1127/
- The Industry Life Cycle in an Economic Downturn: Lessons from Firm’s Behavior in Spain, 2007–2012 – Journal of Business Cycle Research – https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s41549-020-00048-w
- Navigating the S-Curve In Your Business | C12 – https://www.joinc12.com/leadership/navigating-the-s-curve-in-your-business/
- Navigating the Product Life Cycle: Key Strategies for Every Stage – https://startup-house.com/blog/product-life-cycle-strategies
- From Growth to Decline: How Industry Life Cycles Shape Business Strategy – https://ibisworld.com/blog/industry-life-cycles/
- The Benefits Of Using An Industry Life Cycle When Analyzing Startups – FasterCapital – https://fastercapital.com/topics/the-benefits-of-using-an-industry-life-cycle-when-analyzing-startups.html
- Future-Proofing Your Business – How Adaptive Strategy Can Help You Thrive in Uncertain Times – https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/future-proofing-your-business-how-adaptive-strategy-can-help-lyfjf
- Deep Dive into Economic Life Cycle and Value-Creating Growth Strategies – https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/deep-dive-economic-life-cycle-value-creating-growth-sanjeev-isllf
- Product Life Cycle: Moving from Theory to Practice – https://www.bu.edu/bhr/2015/02/02/product-life-cycle-moving-from-theory-to-practice/